

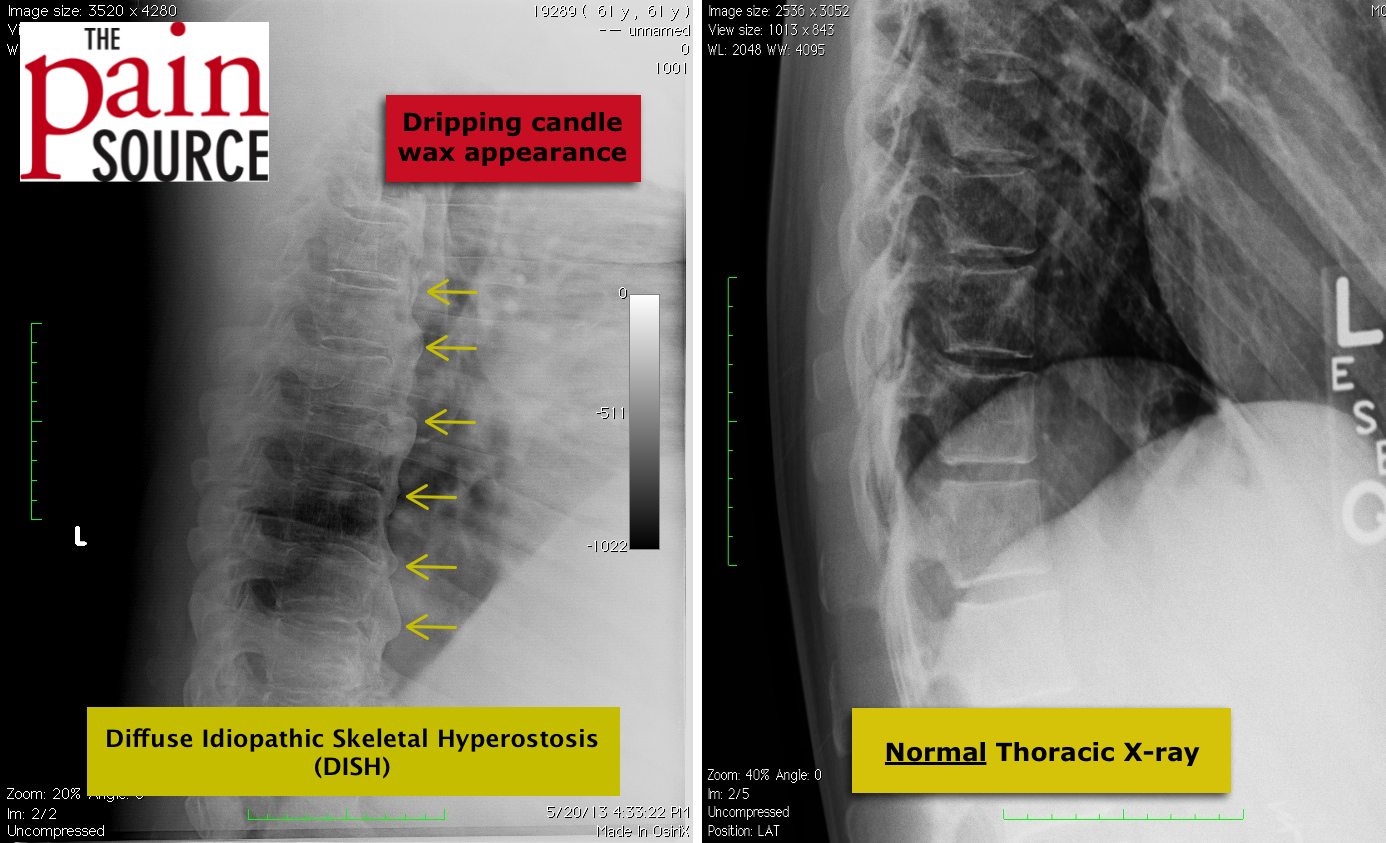
bone spurs) presses upon one of the nerves that allow the vocal cords to move (e.g. Difficulty swallowing or hoarse voice: Hoarse voice can occur if one of the outgrowths of bone (e.g.Other possible symptoms of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis include the following. It is undetermined whether the pain occurs because of inflammation or chronic bone changes and bone growth over time. It can occur at rest but may also occur when pressure is applied to any of the affected body parts. Pain has also occasionally been reported to occur prior to the development of changes on X-ray. Pain may also occur in the shoulders, elbows, knees, or heels. Pain: Pain is most common in the neck or upper back of the spine.It is common for this stiffness to recur as movement subsides in the evening. Swelling can limit the ability of the spine to move until it is disrupted by movement upon waking. During sleep, you move less than when you’re awake and the joints of the spine can become mildly inflamed. Stiffness/Loss of range of motion: Stiffness is usually worse in the morning and it is typical to experience a loss of range of motion in the back.The main symptoms of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis include the following. This disease is managed with pain medication, physiotherapy, and, in rare cases, surgery.ĭiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis symptoms Main symptoms You should visit your primary care physician who will be able to confirm the diagnosis with X-ray, and localize the problem to specific areas in your spine. Treatment focuses on addressing overall health to limit the progression of the disease as well as supportive measures for specific symptoms. Other symptoms include difficulty swallowing or hoarseness, spinal fractures, and tingling or numbness in the lower legs or even paralysis. upper back) that generally gets worse over time and can become severe and debilitating. This condition may cause no symptoms whatsoever, or it may cause mild to moderate stiffness or pain in the thoracic spine (e.g.

Bone may grow excessively in other areas of the skeleton including the shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, ankles, feet, hands, and ribs. Bone can also form in other areas and on other types of connective tissues like tendons (e.g. cords connecting two bones) connect the bones of the spine (e.g. In particular, bone forms most frequently at areas where ligaments (e.g. Establishment of a national multicenter DIPNECH registry would allow formulation of optimal evidence-based guidelines for management of these patients.What is diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis?ĭiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is a disorder in which bone forms on areas where it should not. Long-term follow-up and treatment remains incomplete. In general, the clinical course remains stable however, progression to respiratory failure does occur. The majority of patients presenting with DIPNECH are middle-aged females with symptoms of cough and dyspnea obstructive abnormalities on pulmonary function testing and radiographic imaging showing pulmonary nodules, ground-glass attenuation, and bronchiectasis. Available follow-up data in 17 patients showed 6 clinically improved, 7 who remained stable, and 4 clinically deteriorated.
Treatments strategies included systemic and inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and lung resection. Histological confirmation required surgical lung biopsy for 88% however, transbronchial biopsies alone were diagnostic in three patients. Lung nodules were seen in 15 patients (63%), ground-glass attenuation in 7 patients (29%), and bronchiectasis in 5 patients (21%). Pulmonary function testing showed obstructive ventilatory disease in 54%. Symptoms included cough (71%), dyspnea (63%), and wheezing (25%) occurring days to years before diagnosis. Mean age at diagnosis was 58 years (range, 36-76 yr). Another case from our institution is contributed. Twenty-four DIPNECH cases were identified. A systematic electronic literature search was conducted for adult DIPNECH cases reported in the English literature during the past 6 years. A systematic review is presented, focusing on patient demographics, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment options, and outcomes. Diagnostic and treatment information is limited. Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH) is being recognized with increasing frequency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
